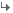Between 1967 and 1993, just a few hundred Palestinians from the West Bank or Gaza won the right to live in Israel by marrying Israeli Arabs (who constitute nearly one-fifth of Israel's population) and acquiring Israeli citizenship. Then the Oslo Accords offered a little-noted family-reunification provision that turned this trickle into a river: 137,000 residents of the Palestinian Authority (PA) moved to Israel in 1994-2002, some of them engaged in either sham or polygamous marriages.
 The Israeli Supreme Court building in Jerusalem. |
Second, it serves as a stealth form of Palestinian "right of return," thereby undermining the Jewish nature of Israel. Those 137,000 new citizens constitute about 2 percent of Israel's population, not a small number. Yuval Steinitz, now the finance minister, in 2003 discerned in PA encouragement for family reunification "a deliberate strategy" to increase the number of Palestinians in Israel and undermine its Jewish character. Ahmed Qurei, a top Palestinian negotiator, later confirmed this fear: "If Israel continues to reject our propositions regarding the borders [of a Palestinian state], we might demand Israeli citizenship."
In response to these two dangers, Israel's parliament in July 2003 passed the "Citizenship and Entry into Israel Law." The law bans Palestinian family members from automatically gaining Israeli residency or citizenship, with temporary and limited exemptions requiring the interior minister to certify that they "identify with Israel" or are otherwise helpful. In the face of severe criticism, then-Prime Minister Ariel Sharon affirmed in 2005 that "The State of Israel has every right to maintain and protect its Jewish character, even if that means that this would impact on its citizenship policy."
 Winston Churchill in 1939. |
Last week, Israel's Supreme Court, by a 6-5 vote, upheld this landmark law, making it permanent. While recognizing the rights of a person to marry, the court denied that this implies a right of residency. As the president-designate of the court, Asher Dan Grunis, wrote in the majority opinion, "Human rights are not a prescription for national suicide."
This pattern of Palestinian emigration toward Jews goes back almost to 1882, when European Jews began their aliyah (Hebrew for "ascent," meaning immigration to the land of Israel). In 1939, for example, Winston Churchill noted how Jewish immigration to Palestine had stimulated a like Arab immigration: "So far from being persecuted, the Arabs have crowded into the country and multiplied till their population has increased."
In brief, you didn't have to be Jewish to benefit from the Zionists' high standard of living and law-abiding society. One student of this subject, Joan Peters, estimates that a dual Jewish and Arab immigration "of at least equal proportions" took place between 1893 and 1948. Nothing surprising here: other modern Europeans who settled in underpopulated areas (think Australia or Africa) also created societies that attracted indigenous peoples.
 Gay parade, Tel Aviv, 2010: how many Palestinians among them? |
The Supreme Court's decision has momentous long-term implications. As Eli Hazan writes in Israel Hayom, "The court ruled de jure but also de facto that the state of Israel is a Jewish state, and thus settled a years-long debate." The closing of the back-door "right of return" secures Israel's Zionist identity and future.
Mr. Pipes (www.DanielPipes.org) is president of the Middle East Forum and Taube distinguished visiting fellow at the Hoover Institution of Stanford University. © 2012 by Daniel Pipes. All rights reserved.
Jan. 18, 2012 update: An poll conducted by the Mina Tzemach Institute finds that an astonishing 83 percent of Israelis are against the Supreme Court's decision discussed above. Something fishy here.
Nov. 25, 2012 update: Another terror attack by a naturalized Palestinian prompts reflections on the 2003 law by Nadav Shragai, "Family reunification? Not in Israel."