What does it mean that Mohamed Morsi is president of Egypt? Speaking for the American consensus, Bret Stephens recently argued in the Wall Street Journal against the consolation that the Muslim Brotherhood's victory "is merely symbolic, since the army still has the guns." He concluded that "Egypt is lost."
We shall argue to the contrary: the election was not just symbolic but illusory, and Egypt's future remains very much in play.
Morsi is not the most powerful politician in Egypt or the commander in chief. Arguably, he does not even run the Muslim Brotherhood. His job is undefined. The military could brush him aside. For the first time since 1954, Egypt's president is a secondary figure, assigned the functionary role long associated with its prime ministers.
 A picture of Morsi and Tantawi reveals the terms of their relationship: Not only is Tantawi sitting on the right side, where prior Egyptian presidents (Nasser, Sadat, Mubarak) ritualistically sat when hosting a visitor, but their meeting took place in the Ministry of Defense, not in the presidential palace, which protocol would normally require. |
Mohamed Tantawi is the real ruler of Egypt. Chairman of the Supreme Council of the Armed Forces (SCAF), Field Marshall, and Minister of Defense, he serves not only as the commander in chief but also as effective head of all three Egypt's governmental branches. Tantawi is an autocrat with near-absolute powers. As chief representative of the military junta that has been ruling Egypt since February 2011, his mission is to extend the junta's rule indefinitely into the future, thereby assuring officers their perquisites and privileges.
SCAF exploits the Muslim Brotherhood and other proxies as its civilian fronts, a role they are happy to play, by permitting Islamists to garner an outsized percentage of the parliamentary vote, then to win the presidency. During the suspicious week-long delay before the presidential votes were announced, SCAF met with the Muslim Brotherhood's real leader, Khairat El-Shater, and reached a deal whereby Morsi became president but SCAF still governs.
To understand SCAF's power, note three actions it took in conjunction with the presidential elections:
Imposition of martial law: On June 13, the Justice Minister authorized the General Intelligence Services and military police to arrest civilians at will and incarcerate them for six months if they express any form of written or artist opposition against SCAF, the police, or their Islamist proxies, while protesting these same institutions on the streets can lead to life in prison.
Dissolution of parliament: On the grounds that the parliamentary elections of Nov. 2011-Jan. 2012, breached the constitution (which prohibits party candidates to run for "individual" seats), the Supreme Administrative Court ruled them invalid in February 2012. On June 14, the SCAF-controlled Supreme Constitutional Court confirmed this decision and dissolved parliament. In retrospect, it appears that SCAF, which oversaw those elections, intentionally allowed Islamists to break the law so as to have an excuse at will to dissolve Egypt's fraudulent parliament.
Establish the premise for martial law: SCAF issued a constitutional declaration on June 17 that formalized its intention to prolong the military's 60-year-old rule. Article 53/2 states that, in the face of internal unrest, "the president can issue a decision to direct the armed forces – with the approval of SCAF - to maintain security and defend public properties." The basis for a complete military takeover could hardly be more baldly asserted; Morsi's plan to reconvene the dissolved parliament could justify such an action.
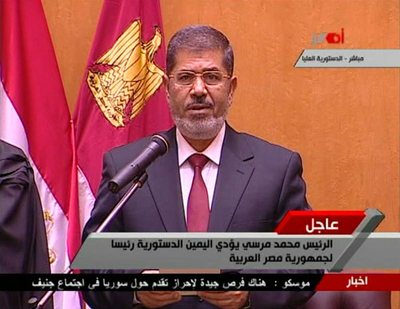 Morsi took the oath of office before the Supreme Constitutional Court and not before the parliament. Score another symbolic victory for SCAF. |
If foreigners are largely blind to SCAF's power play, Egyptians widely recognize this reality. The liberal April 6 Youth Movement called its recent actions "a soft coup d'état." Journalist Zainab Abu El-Magd bitterly noted that "political coups these days are done through 'fair elections'." Ziad Abdel Tawab of the Cairo Institute for Human Rights Studies calls the dissolution of parliament a "blatant military coup." One Egyptian newspaper called Morsi "president without powers," while an Islamist compared him to Queen Elizabeth II of Britain.
SCAF is struggling to perpetuate the status quo, whereby the officer corps enjoys the good life and the rest of the country serves its needs. Making Morsi the apparent president of Egypt cleverly saddles him with responsibility as the country's economic problems worsen. But SCAF's tricks run great dangers and could backfire, for a population fed up with tyranny and backwardness finds itself with more of the same. The next explosion could make the uprising of early 2011 look tame.
To help avoid that next explosion, Western governments should adopt a policy of pressuring SCAF gradually to permit increasing genuine political participation.
Mr. Pipes is president of the Middle East Forum and Taube fellow at the Hoover Institution. Ms Farahat, a fellow at the Forum, also works at the Center for Security Policy and Coptic Solidarity. © 2012 by Daniel Pipes and Cynthia Farahat. All rights reserved.
July 11, 2012 addenda: (1) This is the third in a series by Cynthia Farahat and myself on Egyptian electoral fraud, following on "Egypt's Sham Election" and "Don't Ignore Electoral Fraud in Egypt."
(2) Here's a poetic description of the new president's predicament, by Jeffrey Fleishman and Reem Abdellatif of the Los Angeles Times: "Morsi was elected president without a constitution and with scant defined powers, arriving at the palace as if an accidental figure cast upon a shifting board game."
(3) Morsi appears already to have capitulated to SCAF on the parliament issue, announcing obliquely that "If yesterday's constitutional court ruling prevents parliament from fulfilling its responsibilities, we will respect that because we are a state of the law. There will be consultations with (political) forces and institutions and the supreme council for legal authorities to pave a suitable way out of this," came a statement from his office.
(4) As Tom Stoppard has written, "It's not the voting that's democracy, it's the counting."
Aug. 10, 2012 update: Morsi's firing of Tantawi and replacing him with Abdul Fattah al-Sisi, the director of Military Intelligence and Reconnaissance, comes as a surprise. But it does not conflict with the basic argument above that the military, not the politicians, are the ultimate powerbrokers in Egypt. From what one can tell from the outside, Tantawi lost the support of his fellow military chieftains, particularly those in the Supreme Council of the Armed Forces, and this offered an opening to Morsi to dump Tantawi. But Morsi paid a heavy price for this change, giving the military in return yet more autonomy and privileges than it had enjoyed previously, a price that could come back to haunt him. So, the name on the door has changed but the fundamentals remain the same.
Aug. 18, 2013 update: For more on a topic initiated here about the accuracy of the May 2012 election, see "Evidence that Morsi Actually Lost the Egyptian Presidency."
Mar. 2, 2021 update: The Saudi ambassador to Egypt in 2012, Ahmad Kattan, states that Ahmad Shafik, not Muhammad Mursi, won Egypt's presidential elections that year, and the results were fixed under U.S. pressure.